Presents
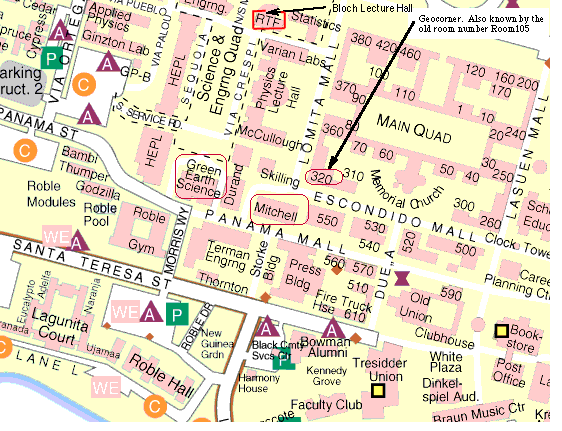
Location: Stanford University
This will be the 425th meeting since 1954

Studies of Late Pleistocene megafaunal fossils and their ancient DNA from Beringia (eastern Siberia, Alaska, and the emerged Bering Strait) indicate sharp declines in steppe bison population diversity and horse body size, extinction of the Alaskan wild ass, and local extinctions of brown bear and woolly mammoth genetic lines beginning at about 37 ka B.P. Beringia is also well known for its remarkably preserved Late Pleistocene frozen animal mummies. 14C ages of these mummies are bimodally distributed, having peaks coincident with the earlier ~37 ka B.P., and ~13 ka B.P. Younger Dryas, onset extinction events. Associated with the ~37 ka B.P. event are, for example, the Berezovka mammoth, headless Selerikan horse, steppe bison “Blue Babe”, and baby mammoths “Dima” and “Lyuba”. Analyses of these and other mummies indicate that they died instantly, in mostly healthy condition, with gut contents and high fat reserves indicative of a late summer to autumn season. An assortment of uneaten limbs and other body parts from a variety of species have also been found. Uniformitarian death scenarios inadequately account for the lack of evidence of normal predation and scavenging. Extensive internal injuries (e.g. large bone fractures, hemorrhaging) and apparent rapid burial of the mummies also indicate that something truly unusual happened at the time of these extinction events. We have discovered what appear to be micrometeorites embedded in seven Alaskan mammoth tusks and a Siberian bison skull acquired from commercial sources. 14C ages for five of these fossils have a weighted mean age of 33 ± 2 ka B.P. Laser ablation ICP-MS and XRF analyses of the particles indicate high Fe contents with compositions enriched in Ni and depleted in Ti, similar to Fe meteorites and unlike any natural terrestrial sources. Microprobe analyses of a Fe-Ni sulfide grain from tusk 2 also show that it contains between 3 and 20 weight percent Ni. SEM images and XRF analyses of a bison skull fragment show sharp-edged channels (~0.1 mm across) containing Fe sulfide material with botryoidal texture that might have cooled from a molten state. Multiple embedded particles are observed on only one side of the tusk and skull fossils, consistent with micrometeorites coming from a single direction. We propose that the extinctions, embedded micrometeorites, and frozen mummies contemporaneous with the ~37 ka B.P. event all resulted from an airburst (similar to the 1908 Tunguska event), or series of airbursts, across Beringia due to the breakup and deep atmospheric penetration of comet or asteroid bodies. The micrometeorites can be envisioned as shrapnel traveling within the blast wave(s). The instantaneous deaths, internal injuries, and possible traumatic amputations and decapitations in megafaunal mummies are consistent with blast injuries related to such a catastrophic scenario.

Jon Hagstrum
Jon received his BA from Cornell University in 1976 his MS from The University of Michigan in 1979, and his PhD from Stanford University in 1985. Since 1979, he has worked as a research geophysicist with the USGS at Flagstaff, Ariz., Denver, Colo., and, beginning in 1981, Menlo Park, Calif. JonŐs work lies primarily within the fields of paleomagnetism, rock magnetism, geomagnetism, structural geology and plate tectonics, but more recently his research subjects have included the avian navigational map, the geological effects of large-body oceanic impacts, and possible impact events around the time of the Younger Dryas abrupt climate event.
Reservations: The preferred way to make reservations is simply to email John Spritzer at jspritzer@usgs.gov by June 3, tell him you will attend, commit to pay, and bring your payment to the meeting. John always emails a confirmation; if you don’t get one, assume email crashed yet again and email him a second time. A check made to “PGS” is preferred, payable at the meeting.
If you want to pay in advance:
Everyone (including Stanford folks now) Please make dinner reservations by June 3. Contact John Spritzer, at U.S. Geological Survey, 345 Middlefield Road, MS-973 Menlo Park, CA 94025, Tel.: (650) 329-4833. Send check made out to “PGS” to John.
Dinner is $35.00. Includes wine (5:30 to 6:15 PM.) and dinner (6:15-7:30 PM.).
For students from all universities and colleges, the dinner, including the social 3/4-hour, is $8.00 and is partially subsidized thanks to the School of Earth Sciences, Stanford University (Note, no-show reservations owe the full price).
Doris, whose wonderful crew prepares our meals, asked that we let you know that people who are late RSVPing and people who show up without a reservation will be welcome but that they will be eating on paper plates with plastic utensils (food supply permitting).
Dues for Academic Year 2010-2011 ($10.00) should be sent to John Spritzer, U.S. Geological Survey, 345 Middlefield Road, MS-973 _Menlo Park, CA 94025. John’s phone: (650) 329-4833.
Officers: Jon Hagstrum, President; David Bedford, Vice President; Mike Diggles, Secretary; John Spritzer, Treasurer; Elizabeth Miller, PGS Stanford University Coordinator
Date created: May 31, 2011
Last modified: May 31, 2011
Created by: Mike Diggles, Webmaster-Secretary, PGS.